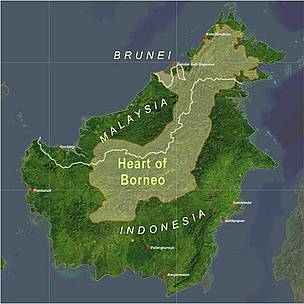
The “Heart of Borneo” is a 220,000 sq km area of protected biodiversity on the Southeast Asian island of Borneo, the third largest island in the world. The initiative is a joint effort by the governments of Brunei Darussalam, Indonesia and Malaysia in establishing a conservation plan for the region’s tropical rainforest and unique wildlife.
The region is the source of 14 of the island’s 20 major rivers and is considered one of the most important centres of biological diversity in the world. It is home to the orangutan, the largest tree-climbing mammal and the only great ape found in Asia, as well as gibbons, macaques, and other primate species. The eastern Sumatran rhinoceros, considered the most critically endangered rhinoceros species in the world, and the Borneo pygmy elephant live in the northeastern part of the conservation area.
Central to the success of the “Heart of Borneo” will be the transboundary collaboration of governments, the engagement of local interests in short and long term planning, securing long term finance, and the cooperation of the private sector in positively contributing to sustainable resource management.
More information on the Heart of Borneo can be found here.
THREE COUNTRIES ONE VISION
HEART OF BORNEO
 v
v